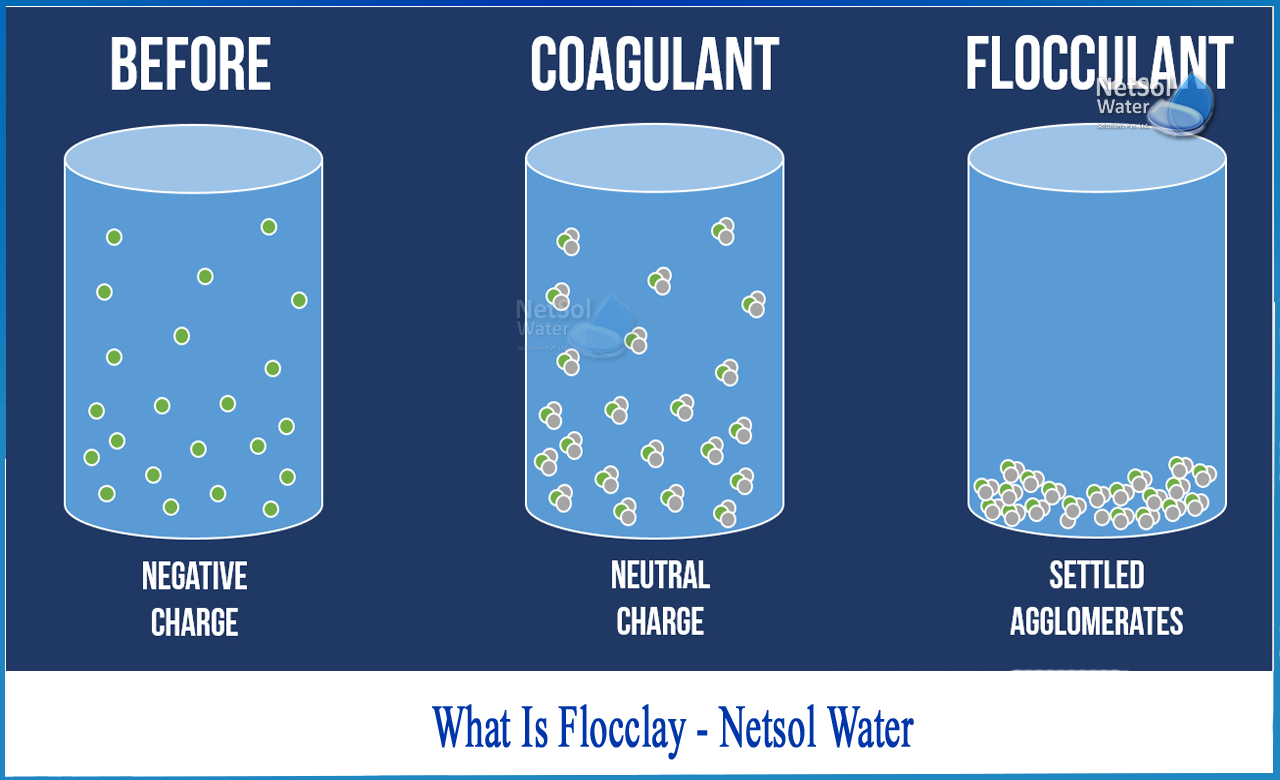
In Kev Kho Dej Pov Tseg Hauv Kev Lag Luam, yuav muaj ntau cov khoom me me uas nyob hauv cov dej khib nyiab. Yuav kom tshem tawm cov khoom me me no thiab ua kom cov dej ntshiab thiab rov siv dua, nws yog ib qho tsim nyog yuav tsum sivCov Tshuaj Ntxiv Rau Dej -Cov tshuaj flocculant (PAM) ua kom cov khoom me me no uas raug tshem tawm cov khoom tsis huv sib sau ua ke ua cov molecules loj thiab nyob hauv.
Cov khoom me me hauv dej yog me me, thiab qhov chaw yog hydrated thiab them kom lawv ruaj khov. Tom qab ntxiv cov flocculant rau hauv dej, nws yog hydrolyzed rau hauv ib qho charged colloid thiab nws cov ions nyob ib puag ncig los tsim cov micelles nrog cov qauv hluav taws xob ob txheej.
Txoj kev sib xyaw sai sai tom qab kev siv tshuaj yog siv los txhawb kom muaj feem thiab ntau zaus ntawm kev sib tsoo ntawm cov khoom me me hauv dej thiab cov micelles tsim los ntawm kev hydrolysis ntawm flocculant. Cov khoom me me hauv dej ua ntej poob lawv qhov kev ruaj khov nyob rau hauv qhov kev ua ntawm flocculant, tom qab ntawd coagulate nrog ib leeg rau hauv cov khoom loj dua, thiab tom qab ntawd nyob hauv lossis ntab hauv qhov chaw sib cais.
Cov khoom GT ntawm qhov ceev gradient G tsim los ntawm kev sib xyaw thiab lub sijhawm sib xyaw T tuaj yeem sawv cev rau tag nrho cov lej ntawm kev sib tsoo ntawm cov khoom me me hauv lub sijhawm teb, thiab cov nyhuv ntawm kev sib xyaw ua ke tuaj yeem tswj tau los ntawm kev hloov tus nqi GT. Feem ntau, tus nqi GT raug tswj ntawm 104 thiab 105. Xav txog qhov cuam tshuam ntawm qhov concentration ntawm cov khoom me me ntawm kev sib tsoo, tus nqi GTC tuaj yeem siv ua tus qauv tswj hwm los piav qhia txog cov nyhuv coagulation, qhov twg C sawv cev rau qhov concentration ntawm cov khoom me me hauv cov dej phwj, thiab nws raug pom zoo tias tus nqi GTC yuav tsum nyob nruab nrab ntawm 100 lossis ntau dua.
Cov txheej txheem ntawm kev ua kom cov flocculant kis mus rau hauv dej sai sai thiab sib tov sib npaug nrog txhua yam dej khib nyiab hu ua kev sib tov. Cov khoom tsis huv hauv dej cuam tshuam nrog cov flocculant, thiab los ntawm cov txheej txheem xws li kev nias ntawm ob txheej hluav taws xob thiab kev ua kom tsis muaj hluav taws xob, qhov ruaj khov ploj lossis txo qis, thiab cov txheej txheem ntawm kev tsim cov micro flocs hu ua coagulation. Cov txheej txheem ntawm kev sib sau ua ke thiab kev tsim cov micro flocs loj hlob mus rau hauv cov flocs loj los ntawm cov txheej txheem xws li kev sib txuas adsorption thiab kev ntes cov sediment hauv qab kev sib xyaw ntawm cov khoom sib txuas thiab dej ntws hu ua flocculation. Kev sib tov, coagulation thiab flocculation yog hu ua coagulation. Cov txheej txheem sib tov feem ntau ua tiav hauv lub tank sib tov, thiab coagulation thiab flocculation raug nqa tawm hauv lub tank tshuaj tiv thaiv.
Txog kev sivPolyacrylamidethiab nws cov flocculation, koj tuaj yeem tiv taujKev Tsim Tshuaj Dejkom paub ntau ntxiv
Lub sijhawm tshaj tawm: Lub Kaum Ob Hlis-02-2022